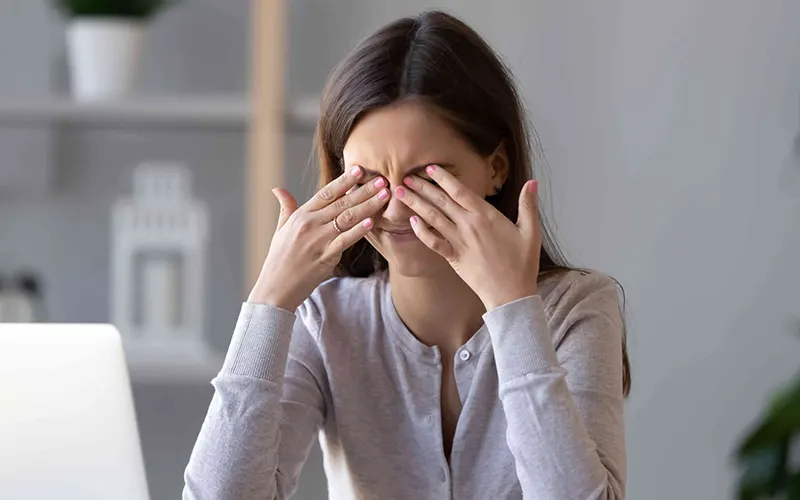
The causes of headaches behind the eyes vary, ranging from eyestrain to migraines. Over-the-counter medications and home remedies can often provide relief, but some cases may necessitate medical attention.
Headaches behind the eyes may affect one or both sides and are frequently accompanied by light sensitivity and other discomforts. Consulting a doctor is essential for identifying the underlying cause and determining the most effective treatment.
Continue reading for further insights into the causes of headaches behind the eyes and strategies for managing them.
Migraine
Migraine is prevalent, impacting nearly 16% of adults in the United States.
Characterized by intense pain typically localized to one side of the head, sometimes behind an eye, a migraine headache can persist for up to 72 hours.
Alongside the headache, individuals may encounter symptoms such as dizziness, weakness, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, mood swings, and visual disruptions, often referred to as aura.
Causes
The exact cause of migraines remains uncertain in medical circles. Nonetheless, alterations in nerve signaling and ocular blood vessels are believed to be significant contributors to its onset.
Migraine episodes are frequently triggered by external factors. These commonly include:
- Insufficient sleep
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Environmental elements like potent odors, smoke, or flickering lights
- Dehydration
- Excessive consumption of caffeine or alcohol
- Intense emotions such as stress or anxiety
Eyestrain
Computer eye strain, also referred to as digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome, encompasses various vision-related issues. Prolonged screen time often leads to discomfort in the eyes.
In addition to eye discomfort, individuals spending extended periods on screens may encounter:
- Dry eyes
- Headaches
- Neck and shoulder discomfort
- Blurred vision
Discomfort behind the eyes might arise only after prolonged screen exposure, with symptoms alleviating upon cessation. Nonetheless, the incidence of these screen-related symptoms is escalating. Persistent symptoms may necessitate medical intervention.
Causes
Extended periods of screen focus can lead to eye strain, which may also stem from visual issues.
Eye strain commonly arises after prolonged concentration on a single task or object. Additionally, dimly lit surroundings and fatigue can contribute to its occurrence.
Sinusitis
Sinusitis refers to the inflammation or blockage of the sinus passages, which can lead to pressure and discomfort behind the eyes. Depending on the affected sinus cavity, this discomfort may manifest behind one or both eyes.
Additionally, sinusitis can induce pain and pressure in other facial areas, including the forehead and cheeks.
Common symptoms associated with sinusitis include:
- Nasal congestion
- Fatigue
- Exacerbated pain while lying down
- Ache in the upper teeth
Sinusitis is a prevalent condition, typically resolving once the underlying congestion clears, which usually takes 2–3 weeks.
Causes
Allergies or viral infections often trigger sinusitis by causing congestion in the sinus cavities. This congestion can lead to facial pressure and headaches. While bacterial or fungal infections can also cause sinusitis, these instances are commonly linked to immune deficiencies, such as HIV.
Furthermore, sinus pain and pressure can result from nasal polyps or dental procedures.
Cluster Headaches
Cluster headaches are characterized by brief, intense headaches occurring between one to eight times a day, typically on one side of the head. These headaches often induce a sharp or throbbing pain behind a single eye.
In addition to the headache, accompanying symptoms often manifest on the same side, including:
- Nasal congestion or a runny nose
- Facial flushing
- Excessive sweating
The timing of cluster headache episodes varies, but they frequently occur during the night.
Causes
The precise cause of cluster headaches remains uncertain, and extensive research on the topic is lacking. However, these headaches are not uncommon.
While the exact mechanisms are unclear, researchers hypothesize a potential gender disparity, with males experiencing cluster headaches more frequently than females. Additionally, there might be a genetic predisposition, resulting in some individuals being at a higher risk than others.
Tension Headaches
Tension headaches rank as the most prevalent type of headache, with a higher incidence among females than males.
While some individuals experience tension headaches once or twice monthly, others encounter them more frequently. When this pattern persists for three months or beyond, medical professionals classify the headaches as chronic.
Typically, tension headaches provoke pain behind both eyes and a sensation of pressure across the forehead. They can emerge at any moment and endure from 30 minutes to several hours. In severe instances, symptoms of a tension headache may linger for several days.
Furthermore, tension headaches may elicit scalp tenderness. The pain associated with these headaches tends to be dull, often centered in the forehead and radiating to the neck.
Causes
Tension headaches stem from various triggers, such as:
- Sleep deprivation
- Stress
- Prolonged screen exposure
- Extended periods of driving
- Muscle contractions in the neck or head
Read More : Insights on Migraine in the Aging Process
Treatment Options for Headaches Behind the Eyes
For mild to moderate headaches, over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are often effective, though severe pain may necessitate prescription medication.
In cases of frequent migraine headaches, doctors may prescribe antidepressants, antiseizure medications, or oral contraceptives as preventive measures. During a migraine episode, resting in a dark room can offer relief, and applying a cool, damp cloth over the eyes may provide additional comfort.
Short-term use of muscle relaxants can help manage tension headaches.
When bacterial sinusitis triggers headaches, antibiotics are typically prescribed. Alternatively, nasal decongestant sprays are recommended for sinusitis resulting from allergies or viral infections.
Home Remedies
Managing the underlying causes of headaches behind the eyes can be effectively done at home.
To potentially prevent migraine onset, consider avoiding the following triggers:
- Loud noises
- Strong odors
- Alcohol consumption
- Hunger
- Stress
- Fatigue
- Bright lights
- Sleep deprivation
For alleviating discomfort associated with tension headaches behind the eyes, try implementing these strategies:
- Minimize muscle strains in the head and neck
- Practice stress management techniques
- Ensure adequate nightly sleep
- Reduce screen time exposure
When sinusitis is the culprit behind eye-related headaches, consider the following approaches:
- Limit or abstain from caffeine intake
- Avoid alcohol consumption
- Refrain from tobacco use
- Incorporate regular exercise into your routine
- Minimize intake of processed foods
When to Seek Medical Attention
Individuals experiencing frequent headaches behind the eyes should seek medical attention. A doctor may advise an eye examination and prescribe treatments not readily available over the counter (OTC).
Implementing lifestyle changes may also aid in preventing recurring pain.
In Summary
Headaches behind the eyes, often accompanied by other symptoms, can be distressing. They can arise from various health conditions, with pinpointing the cause being the initial step toward treatment.
Avoiding specific triggers like alcohol, caffeine, and tobacco, along with making lifestyle modifications, may offer relief.
Consulting a doctor is crucial for identifying the root cause and receiving additional support, including medication.